Microscopy and Spectroscopy Lab (A-1)
To do state of art science, we need state of art facilities. Such a facility has been developed at the Department of Physics which includes the advanced equipment to do the imaging as well as spectroscopic analysis.
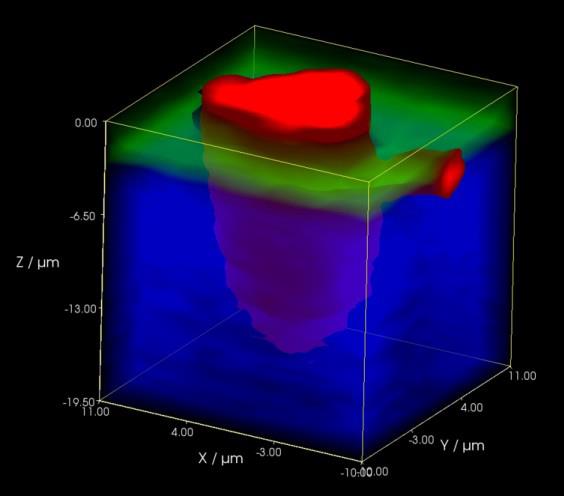
Atomic Force Microscope
Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) was pioneered in 1986 by Nobel Prize Winner Gerd Binnig along with Calvin Quate and Christophe Gerber. It provides three dimension-al topographic information about a sample by probing its surface structure with a very sharp tip. The tip is scanned laterally across the surface, and the vertical movements of the tip are recorded and used to construct a quantitative 3-D topographic map

Applications
- High-resolution surface profilometry
- Surface roughness measurements
- Pit analysis for optical disk storage media
- Semiconductor device structural analysis
- Surface cleaning and polishing studies
- Phase separation in polymers
- Magnetic domain and surface roughness analysis for computer hard-disks
- Investigation of local mechanical properties (stiffness, adhesion,
friction)
- High-resolution imaging of biological samples
- Studies of Nano-scale forces
Download Posters
UV/Vis/ NIR Spectroscopy
The UV-Vis spectrometry is one of the oldest instrumentals techniques of analysis and is the basis for a number of ideal methods for the determination of micro and semi-micro quantities of analytes in a sample.
UV-Vis spectrum results from the interaction of electromagnetic radiation in the UV-Vis region with molecules, ions, or complexes. It forms the basis of analysis of different substances such as inorganic, organic and biochemical.
These determinations find applications in research, industry

Working Principle of Spectroscopy
- The principle is based on the measurement of spectrum of a sample containing atoms / molecules.
- Spectrum is a graph of intensity of absorbed or emitted radiation by sample verses frequency (ν) or wavelength (λ).
- Spectrometer is an instrument design to measure the spectrum of a compound.
1. Absorption Spectroscopy:
- An analytical technique which concerns with the measurement of absorption of electromagnetic radiation.
- e.g. UV (185 - 400 nm) / Visible (400 - 800 nm) Spectroscopy, IR Spectroscopy (0.76 - 15 μm).
2. Emission Spectroscopy:
- An analytical technique in which emission (of a particle or radiation) is dispersed according to some property of the emission & the amount of dispersion is measured.
- e.g. Mass Spectroscopy
Applications of UV/Vis/NIR Spectroscopy
- Identification of various organic, inorganic molecules and ions by matching their spectrum with reference spectra.
- For qualitative and quantitative analysis of drugs in pharmaceutical industry.
- Monitoring of reaction rates (chemical kinetics)
- Enzyme assays
- Environmental remote sensing
Spectroscopy in Different Fields
UV-Vis Spectrometry is commonly used in different fields such as:
- Research
- Industry
- Clinical Laboratories
- Chemical Analysis of Environment
- Pharmaceutical
- Agriculture (analysis of food coloring)
Download Posters
Raman-PL cutting edge Applications
Raman spectroscopy can pro-vide the key information about the chemical composition and material structure.

The Raman effect results from the interaction of laser light with molecular vibration within the sample, and highly sensitive to the small change in chemistry and molecular environment.
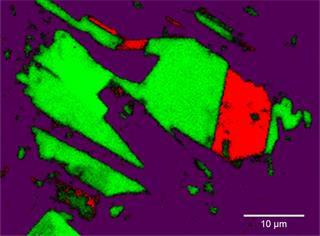
Life sciences
Disease diagnostic, dermatology, cell screening, Cosmetics, micro-biology, protein investigation, drug interaction, ageing and neurodegenerative diseases, bio-fuel and agricultural research and many more Raman spectroscopy offer new methods of characterization in life sciences
Material sciences
Raman spectroscopy most properly the ideal available tool for the investigating new materials used in the nanotechnology. Raman spectroscopy playing a leading role in developing photovoltaic technologies.
Chemical sciences
Raman analysis enables you to identify the chemicals, as well as the quantitative and qualitative measurements about them. Raman sys-tem provides you with the power to investigate all types of polymers. Raman plays a key role from drug discovery, formulation and trouble shooting.
Earth sciences
Raman spectroscopy is used to analyze all types of Geological samples. Raman is used to identify investigate and certify the gem stones.
Analytical Sciences
Raman is used to study a large number of cultural items. Contamination identification is also largest area of Raman's applications. Ra-man systems are used in forensic science laboratories' worldwide.



Download Posters
Downloads